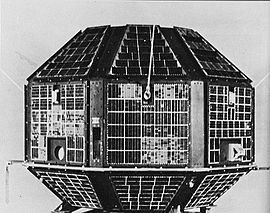
India’s First Satellite Launch: Aryabhata
In 1975, India achieved a significant milestone in its space exploration journey by launching its first satellite, Aryabhata. This historic event took place on April 19, 1975, with the assistance of the USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics). The satellite was named after the ancient Indian mathematician Aryabhata, symbolizing India’s rich scientific heritage and its entry into the space age.
Aryabhata was launched aboard a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from the Kapustin Yar launch site. This collaboration between India and the USSR showcased the strong ties between the two nations and their shared interest in space exploration.
The Significance of Aryabhata
The launch of Aryabhata was a momentous occasion for India, as it marked the country’s first step towards becoming a space-faring nation. It was a proud moment for the entire nation, symbolizing India’s technological prowess and its determination to make its mark in the field of space science.
Although Aryabhata faced a power failure and stopped transmitting data after a few days in orbit, its launch laid the foundation for India’s future space missions and satellite technology research. The knowledge gained from this mission helped Indian scientists and engineers gain valuable insights into the complexities of space exploration.
The launch of Aryabhata also had a profound impact on the country’s scientific community. It inspired a new generation of scientists and engineers to pursue careers in space research and technology. The success of this mission boosted the morale of the Indian scientific community and instilled a sense of national pride.
India’s Space Program: Past, Present, and Future
The launch of Aryabhata was just the beginning of India’s ambitious space program. Over the years, India has made significant progress in the field of space exploration and satellite technology.
Today, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is at the forefront of India’s space program. ISRO has successfully launched numerous satellites for various purposes, including communication, weather forecasting, remote sensing, and scientific research.
One of the notable achievements of ISRO is the Chandrayaan-1 mission, which was launched in 2008. This mission involved sending an orbiter to the Moon, marking India’s first lunar exploration endeavor. The data collected by Chandrayaan-1 has contributed to our understanding of the Moon’s surface and its composition.
ISRO’s Mars Orbiter Mission, also known as Mangalyaan, was another significant milestone in India’s space program. Launched in 2013, Mangalyaan successfully entered the orbit of Mars in 2014, making India the first country to achieve this feat in its maiden attempt.
Looking towards the future, India has several ambitious projects in the pipeline. ISRO is planning to launch the Aditya-L1 mission, which aims to study the Sun’s corona and its impact on space weather. Additionally, ISRO is working on the Gaganyaan mission, which aims to send Indian astronauts to space.
Conclusion
The launch of India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, on April 19, 1975, was a momentous event that marked India’s entry into the space age. Despite facing technical challenges, Aryabhata’s launch laid the foundation for India’s future space missions and satellite technology research.
Since then, India has made remarkable progress in its space program, with ISRO leading the way in satellite launches and space exploration. The success of missions like Chandrayaan-1 and Mangalyaan has put India on the global map of space exploration.
As India continues to push the boundaries of space science and technology, the future looks promising. With ambitious projects like Aditya-L1 and Gaganyaan on the horizon, India is poised to make even greater strides in the field of space exploration.
References:
Excerpt: In 1975, India launched its first satellite, Aryabhata, with the help of the USSR. This significant milestone marked India’s entry into the space age and laid the groundwork for future space missions and satellite technology research.